|
Top page > Forefront of lactic acid bacteria research > Information on 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria > Findings from 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria research(4)
Findings from 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria research(4)A human-subject study indicates that continuous ingestion of 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria may improve the efficacy of influenza vaccines.This study investigated the effects of continuous consumption of yogurt containing 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria on the amount of antibodies (antibody titer) produced in the body against the influenza virus after influenza vaccination. In the study, healthy human subjects were asked to consume yogurt drinks containing 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria every day for 3 weeks prior to influenza vaccination, and the antibody titers produced in their bodies against the influenza virus before and after the vaccination were measured. Changes in antibody value in tests (Type A (H1N1), Type A (H3N2), and Type B)Test on male college students aged 18 to 25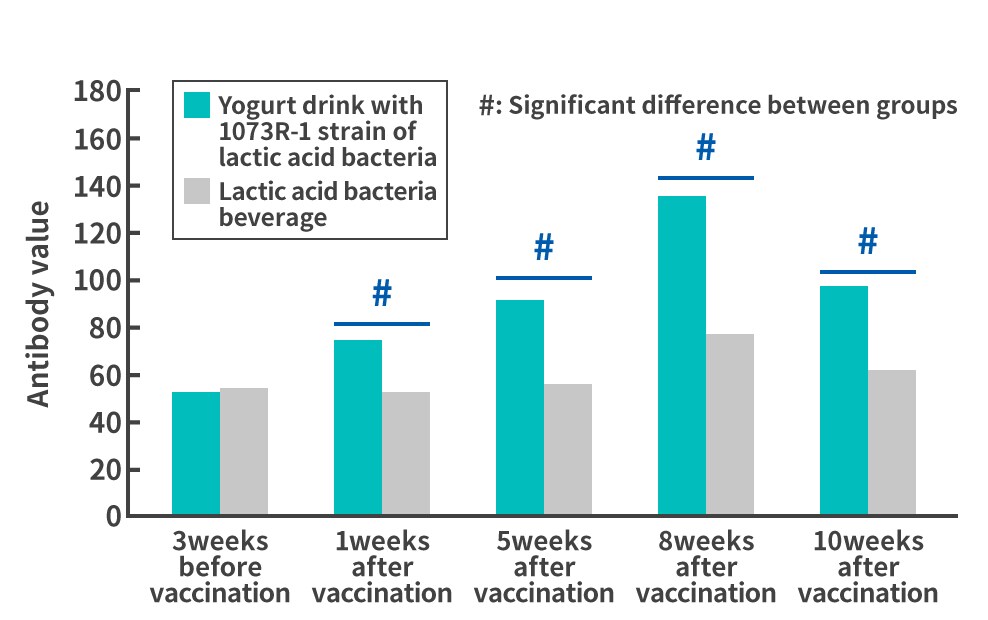 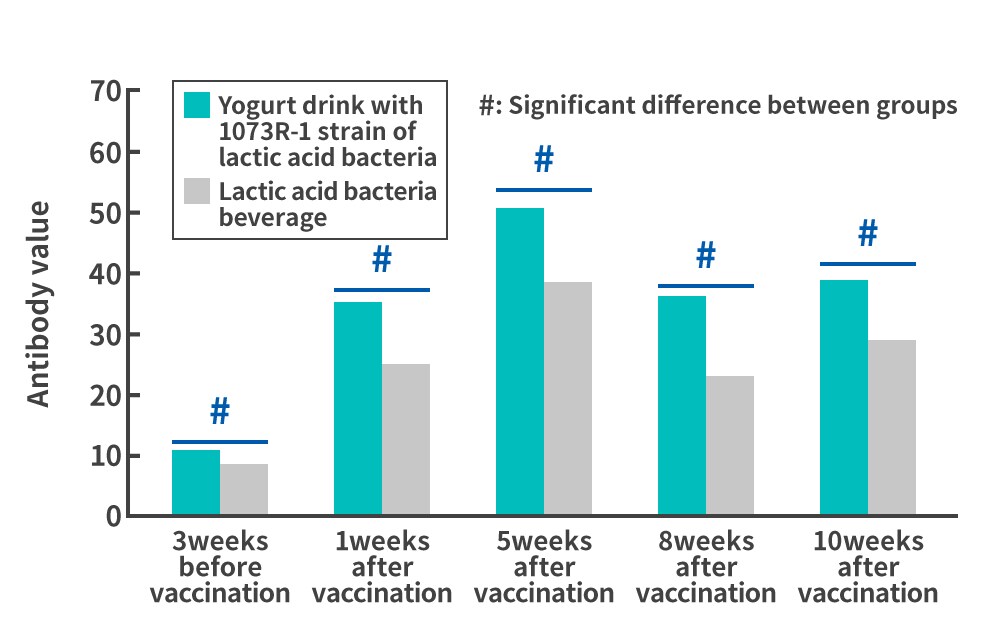
Test on male and female subjects aged 25 to 59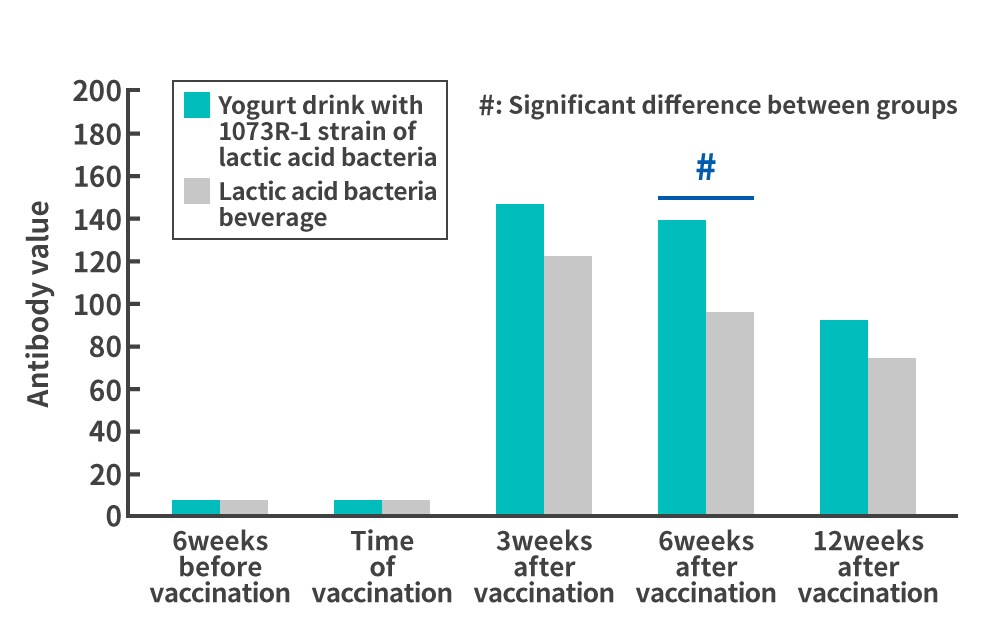 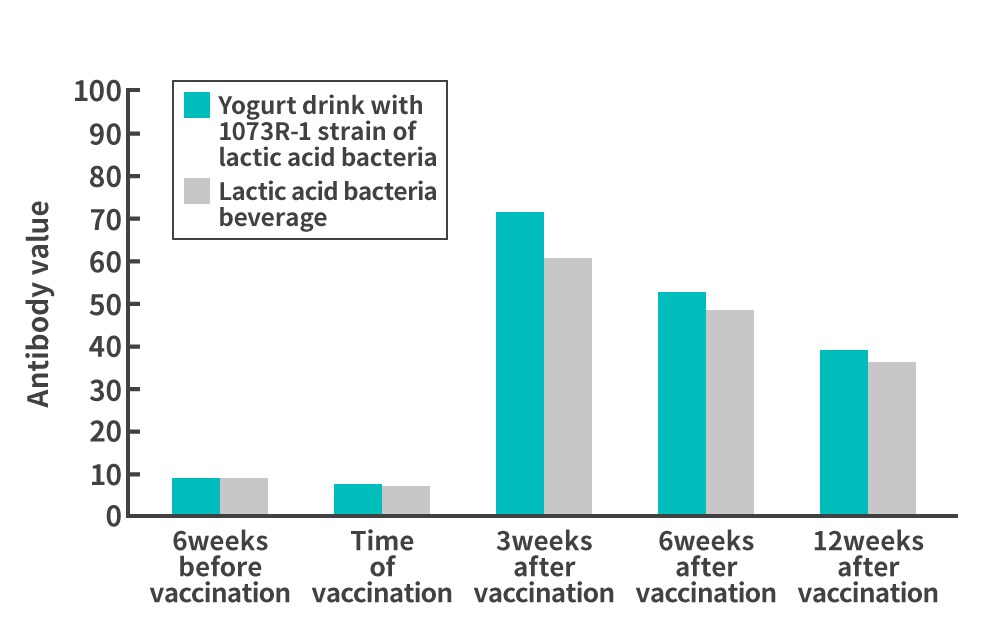 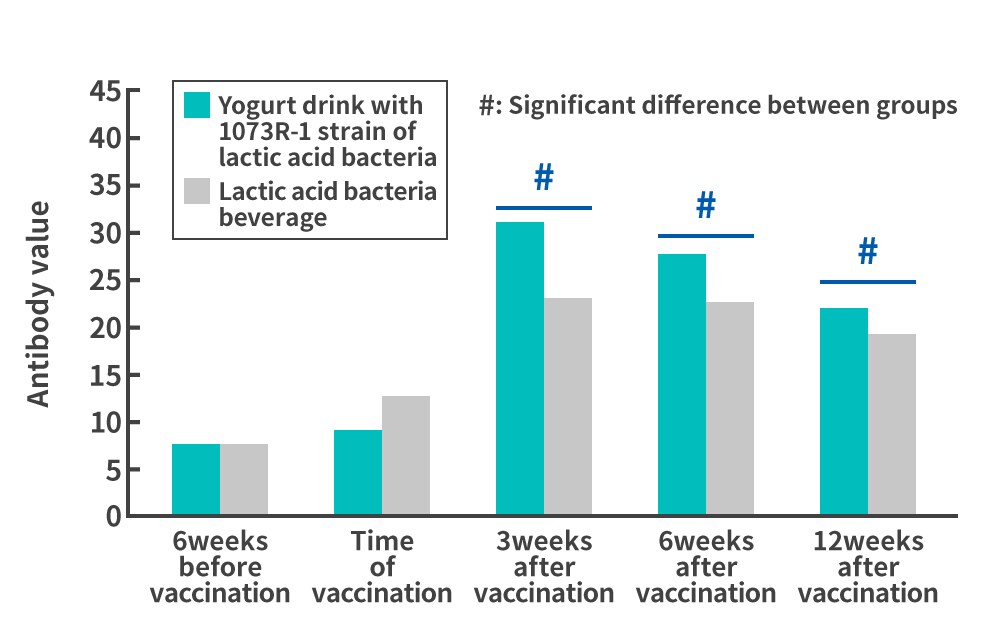
The results showed that those who drank the yogurt drinks containing the 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria daily had higher antibody titers against influenza A H3N2 and B in the study of male college students aged 18 to 25 and against influenza A H1N1 and B in the study of males and females aged 25 to 59, compared to those who drank an unfermented acidic milk beverage (placebo), demonstrating changes that were different from normal. These results suggest that the yogurt containing lactic acid bacterium strain 1073R-1 functions as an adjuvant* which enhances the antibody titer after influenza vaccination, and that it may enhance the effects of influenza vaccination. *Agent that is used together with a vaccine to supplement, enhance, or improve the efficacy of the vaccine. |



