|
Top page > Forefront of lactic acid bacteria research > Information on 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria > Findings from 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria research(2)
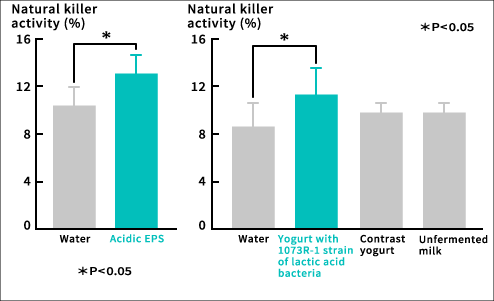
Findings from 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria research(2)A study indicates that feeding mice with 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria increases their NK activity level.Research has shown that there are two types of polysaccharides that are produced by 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria (i.e., exopolysaccharides (EPSs)), one being neutral and the other being acidic. When both types of EPSs were administered to the spleen cells of mice (i.e., cell population consisting of various immune cells), the acidic EPSs displayed a function of sending signals to produce IFN-γ*2, which is an immune messenger. When these acidic EPSs were given to mice, their NK activity increased. Then yogurt containing 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria was fed to mice, and their NK activity also increased in a manner similar to when acidic EPSs were administered. *2: IFN-γ (interferon gamma) is a type of cytokine secreted by T cells that activates macrophages and NK cells and enhances immune strength. Increase in NK activity was observed in miceIngestion of yogurt containing 1073R-1 lactic acid bacteria increased NK activity.
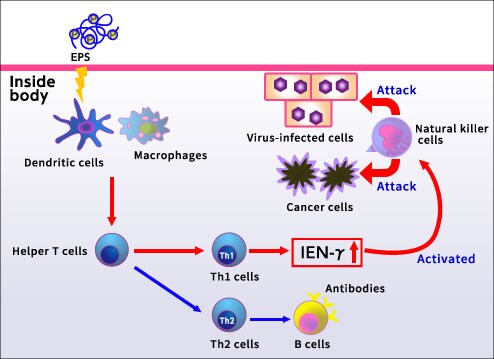
Mechanism of NK activity
Acidic EPSs have an IFN-γproduction-inducing function, while IFN-γ activates NK cells.
|