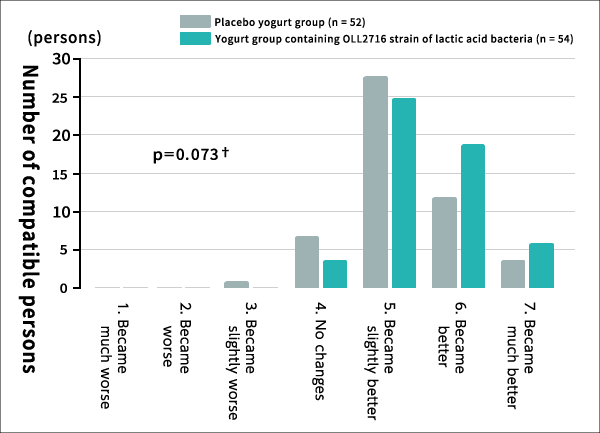|
Top page > Forefront of lactic acid bacteria research > Information on OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria > Results of research on OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria (in relation to FD)
Results of research on OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria (in relation to FD)Effect of OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria to improve FD symptoms① A majority of the subjects in the group that was fed yogurt containing OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria reported improved or significantly improved symptoms.In this study, a total of 106 untreated subjects aged between 20 and 64 with FD symptoms were randomly divided into two groups, and one group was fed yogurt containing OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria (number: 109) once a day (85 g), while the other group was fed yogurt not containing OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria (placebo) in the same amount and with the same frequency, for a period of 12 weeks. After the 12 weeks, a questionnaire survey was conducted to learn about the subjects’ overall impression of the effect of the yogurt on their stomach symptoms. The survey revealed that the first group that was fed yogurt containing OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria for 12 weeks thought their stomach symptoms started to improve more compared to the second group that was given the placebo, while the percentage of those reporting either significantly improved or improved stomach symptoms overall was higher in the first group than the second group by roughly 16 points.
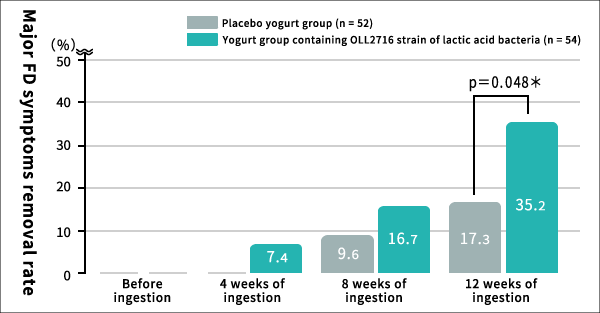
Figure: Comprehensive evaluation of stomach symptom improvement [Evaluation method] ②The rate of disappearance of all four FD symptoms among the OLL2716-fed experimental group after 12 weeks was twice that of the placebo group.In addition, when the ratio of the subjects from which all four FD symptoms disappeared (i.e., elimination rate) was measured at four, eight, and 12 weeks after yogurt ingestion, the elimination rate improved with the passage of time. So, 12 weeks later, the elimination rate for the OLL2716-fed experimental group climbed to 35.2%, which was roughly twice the placebo group’s elimination rate of 17.3%.
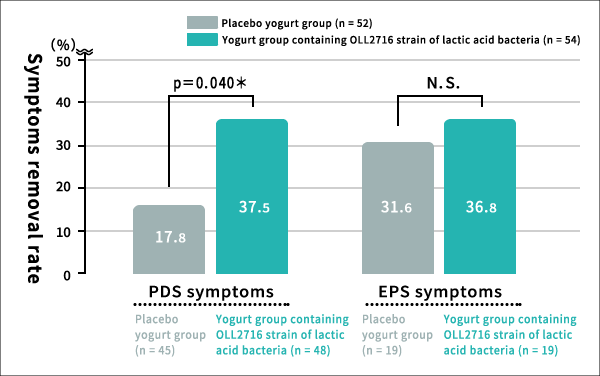
Figure: Change in the elimination rate of all four FD symptoms with time [Evaluation method] ③Of the two FD types, OLL2716 was most effective for postprandial distress syndrome (PDS).Based on the classification of FD into the two types, which are postprandial distress syndrome (PDS) and epigastric pain syndrome (EPS), the subjects were observed from the time they started ingesting yogurt until 12 weeks later to determine the ratio of those from which the symptoms of each FD type were eliminated. It was found that the PDS symptom elimination rate among the experimental group that was fed yogurt containing OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria was significantly high.
Figure: Elimination rates of PDS- and EPS-like symptoms 12 weeks after ingestion of the trial food [Evaluation method] Recap of the study on OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria
【Effect of yogurt containing OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria to improve FD】
Compared to the placebo group, the experimental group that ingested yogurt containing OLL2716 lactic acid bacteria exhibited the following: ●The yogurt appeared to improve the stomach symptoms overall. ●The elimination rate of all four FD symptoms was significantly higher. ●Of the two FD types, the elimination rate was significantly higher for the PDS symptoms. |