What is HbA1c?
About HbA1c
HbA1c is an abbreviation of hemoglobin A1c.
There are three different indicators (targets of measurement) for measuring blood sugar level: fasting (i.e., empty-stomach) blood sugar, postprandial (i.e., post-meal) blood sugar, and HbA1c levels.
As the first two of the three indicators capture momentary values of blood sugar concentration, they only reveal the blood sugar levels present when the blood was drawn. Meanwhile, HbA1c is able to indicate the average blood sugar level of a person over the past one to two months.
Hemoglobin (Hb) – called kesshikiso in Japanese – is a component of red blood cells that transports oxygen throughout the body. Blood is red because that is the color of hemoglobin. When hemoglobin (Hb) binds to glucose in the blood (i.e., blood sugar), HbA1c is formed.
The higher a person’s blood sugar level is (hyperglycemia), the more actively the hemoglobin and blood sugar tend to bind together, and the longer a person remains hyperglycemic, the higher the HbA1c concentration becomes. As such, testing the amount (concentration) of HbA1c in a person’s blood can reveal the average blood sugar level from a certain period in the past.

Source: Glycated hemoglobin | e-Healthnet (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
Where can HbA1c level be tested?
When you take a general medical screening or comprehensive medical examination, the diagnosis report usually includes HbA1c as one of the items. Reportedly, over 5.6% of people tested need some medical attention to improve their HbA1c levels.
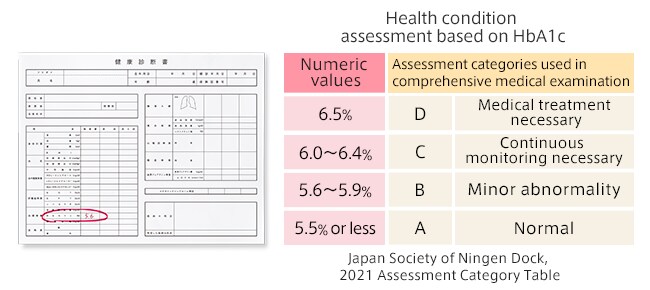
Source: Diabetes | e-Healthnet (Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare)
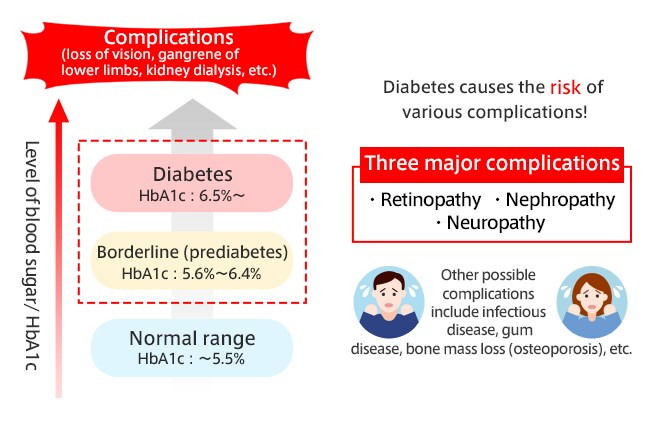
What happens if my HbA1c level is too high?
If you have a high level of HbA1c, it means you have a high risk of diabetes. The criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes are specified based on the level of blood sugar that is chronically high enough to cause microvascular disorders mainly in the form of retinopathy, which is a microvascular complication in the retina of the eyes. Such blood sugar level is 126 mg/dL or higher when fasted and 200 mg/dL or higher two hours after orally ingesting 75 g of glucose. The concentration of HbA1c that corresponds to this level of high blood sugar is 6.5%.
When one has a high level of blood sugar but not high enough to be diagnosed with diabetes, it could still cause various health issues. Many of these health disorders do not occur just because one’s blood sugar level becomes too high at a given time. Rather, they manifest because the blood sugar level – i.e., HbA1c – remains high for a prolonged period, which causes negative physical impacts incrementally and appear as more obvious symptoms in subsequent years.