Findings from OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 lactic acid bacteria research(2)
Yogurt fermented with OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 lactic acid bacteria has been confirmed to enhance NK activity (animal study conducted in 2005).
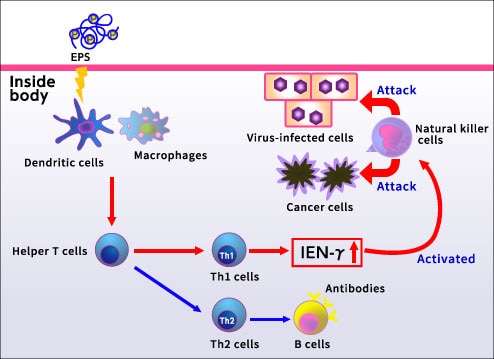
OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 lactic acid bacteria produce polysaccharides (EPSs). When yogurt fermented with OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 lactic acid bacteria was administered to the spleen cells of mice (i.e., cell population consisting of various immune cells), it was found to send signals to produce IFN-γ*1, which is an immune messenger. Then, when yogurt fermented with OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 lactic acid bacteria was administered to mice, NK activity was enhanced.
*1: IFN-γ (interferon gamma) is a type of cytokine secreted by T cells that activates macrophages and NK cells and enhances immune strength.
It was confirmed that NK activity was increased in an animal study.
Yogurt fermented with OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 lactic acid bacteria increased NK activity.

- Study method
- Animal study
- Administration
- The subject pool was divided into the following four groups:
1. Water
2. Yogurt fermented with OLL1073R-1 and OLS3059 lactic acid bacteria
3. Placebo yogurt
4. Unfermented milk - Period of administration
- 4 weeks
- Study period
- 2005
(Source: Makino S, et al. J Dairy Sci. 2006;89(8):2873-81.)
Mechanism of NK activity
EPSs have an IFN-γ production-inducing function, while IFN-γ activates NK cells.
Therefore, ingestion of EPSs is thought to improve immune strength through activation of NK cells.