|
Top page > Forefront of lactic acid bacteria research >
Information on LB81 lactic acid bacteria > New possibilities of LB81 lactic acid bacteria
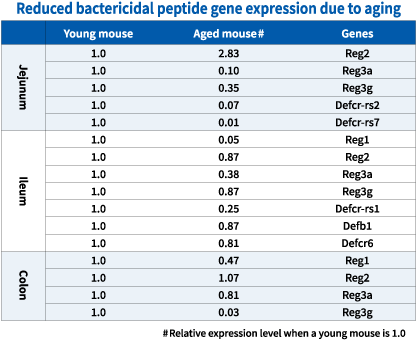
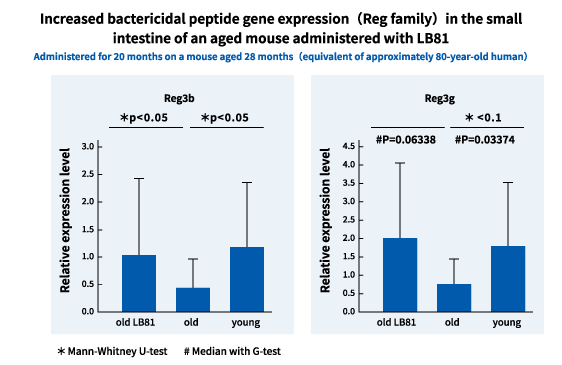
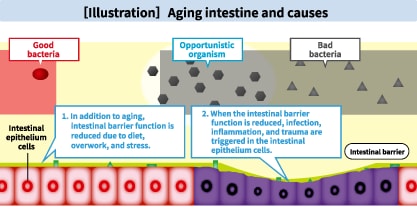
New possibilities of LB81 lactic acid bacteriaJoint research between Meiji Co., Ltd. and the Pasteur Institute identifies two new functions of LB81 lactic acid bacteria. 1. Improve the intestinal barrier function in the intestinal epithelial cellsIt has been proven that LB81 lactic acid bacteria increase the occurrence of antimicrobial peptides, which are a crucial substance known to enhance the barrier function of the intestinal defense mechanism. Healthy intestines are equipped with a defense mechanism, including the layer called the intestinal barrier lining the surface of the intestinal epithelial cells that fends off harmful exogenous agents. However, the intestines of humans living in this day and age are subjected to major challenges in the form of poorly balanced dietary habits burdensome to the digestive tract, stress caused by overwork, irregular lifestyles, etc., aside from the deterioration of function with age. When one’s intestinal functions are diminished by such factors, the substances that support the barrier function decline in number, which in turn weakens the intestinal barrier and increases the risk of attack by cells, pathogens, and other harmful substances. Our research on LB81 lactic acid bacteria has shown that they increase antimicrobial peptides in the intestinal barrier, which are a crucial substance of the barrier being comprised of multiple elements, and enhance the barrier’s function. So, LB81 lactic acid bacteria are thought to act on the intestinal epithelial cells that have been damaged by stress and aging, promote the creation of antimicrobial peptides that maintain the barrier function of the intestines, and keep the intestines healthy and functioning properly.
Summary of the study
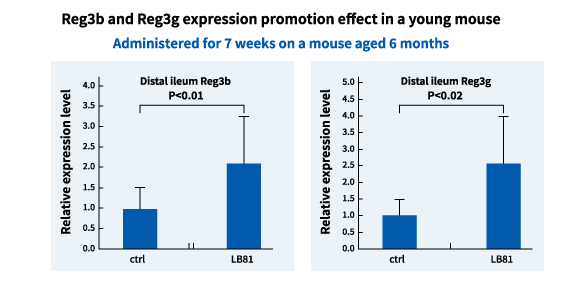
Moreover, when young mice were fed yogurt made from LB81 lactic acid bacteria, increased production of Reg3b and Reg3g was observed as was the case with the old mice, proving that the yogurt enhances the barrier function in both old and young intestines.
<Reference: [Illustration] Intestinal aging and its cause>
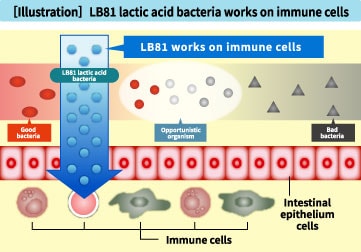
2. Work on immune cells in the intestinesIt has been confirmed that LB81 lactic acid bacteria also affect the immune cells in the intestines. The intestines of a person have a certain condition optimal for age, and are subject to homeostasis that keeps them in the optimal condition constantly. However, when this homeostatic function is compromised due to aging or a pathogen, the person’s immunological homeostasis is also expected to decline. When this study was conducted, it was hypothesized that consumption of LB81 lactic acid bacteria, which are known to improve the balance of intestinal flora consisting of good, bad, and opportunistic bacteria, might support the homeostasis of the intestinal flora and restore immune strength as a result. The study identified the new function of LB81 lactic acid bacteria that positively affects the immune cells in the intestines as well as the intestinal flora.
|




![Reference: [Illustration] Intestinal aging and its cause](/yogurtlibrary/en/laboratory/report/images/lb8103_img_01.jpg)