Current State of Nutrition-related health Issues and
Work to Address them
This section explains the nutrition-related health issues facing the world today, their social and
economic impact, international policies related to them, and the responsibilities required of
food industries.
Current state of nutrition-related health issues
Today, overweight or obesity caused by over-eating and unbalanced diets, have resulted in lifestyle-related diseases, and become a serious nutritional issue around the world. On the other hand, stunted growth, undernutrition, and frailty*1 have increased, due to insufficient protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and other nutrients.

Over-nutrition
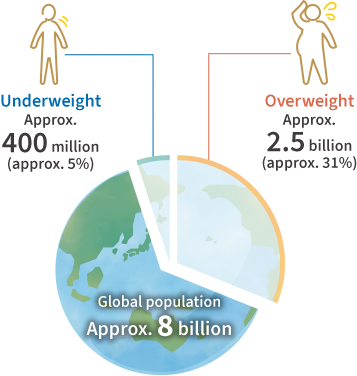
According to research by the World Health Organization (WHO)*2, as of 2022, there were 2.5 billion adults who were overweight, including close to 900 million who were living with obesity.
Overweight and obesity are known to be the causes of many diseases such as high blood pressure, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and cancer.*3
Undernutrition
As stated by the WHO*2, as of 2022, there were approximately 400 million adults in underweight condition. In addition, it is said that over 2 billion adults suffer from micronutrient (vitamins and minerals) deficiencies. Such circumstances are known to trigger various debilitating diseases, and may even cause negative impacts on health.*4
-
*1“Frailty” refers to the decline in physical and cognitive health associated with aging, such as muscle weakness and cognitive function decline. Frailty is generally seen in the older population, and as the level of frailty progresses, it may require long-term care. However, with adequate intervention, frailty can be reversed.
-
*3 GBD 2017 Diet Collaborators, (2019) The Lancet 393 (10184): 1958-72
Impacts from nutrition-related health issues
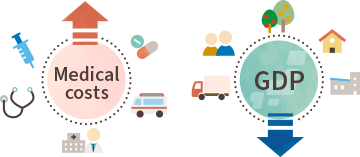
There is concern that they will not only impair people’s health but also have significant social and economic consequences, if these nutrition-related health issues continue untreated. These consequences include increased medical and social security costs as well as reduced labor productivity. In recent years, there has been a growing trend in international policy to address these issues. For instance, the WHO has established nutrition-related targets, and these issues are being positioned as important issues to be addressed at the global level.
Social and economic impacts
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) looked at 52 countries (including OECD, European Union and G20 countries) and predicts that, between 2020 to 2050, countries will spend 8.4% of their health budgets on treading diseases caused by being overweight, and that gross domestic product (GDP) will be reduced by an estimated 3.3% on average due to lower employment and poorer productivity.*5 In addition, the impact of under-nutrition on national productivity and economic growth is estimated to be between 2% and 11% of GDP, although this varies between countries .*6 *7

Trends of international policies
The WHO has set nutrition-related targets for 2025 to reduce risks for mortality owing to poor eating habits. Moreover, the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) established by the United Nations include nutrition and health-related targets such as SDG 2 [Zero hunger] and SDG 3 [Good health and well-being].
Demands on food industries to work to address them
The solution to this nutritional issue requires a better nutritional intake in people’s daily diets. However, it is not easy for individuals to identify the right amount of nutrients and to control their nutritional intake appropriately. Under these situations, food industries that provide daily nutrition through their products need to face this issue seriously. The industries need to actively work to address nutrition-related health issues, such as improving the nutritional value of their products and providing nutritional information.
Responsibilities required of food industries
The food industry is strongly encouraged to develop comprehensive nutrition strategies and strengthen corporate governance for their implementation, as well as to improve transparency in the distribution of information on these matters. NGOs such as the Access to Nutrition Initiative (ATNI) are working to accelerate food industry’s engagement.*7 In addition, the World Benchmarking Alliance (WBA) has a ranking of corporate sustainability related to the food system, Food and Agriculture Benchmark, which sets ‘nutrition’ alongside ‘environment’ and ‘social inclusion’ as an evaluation category.*8

Meiji Nutritional Profiling System (Meiji NPS)
With these backgrounds, Meiji developed the Meiji Nutritional Profiling System (Meiji NPS) as a system that can scientifically evaluate the nutritional value of food. We utilize this system in the development and improvement of products and in providing information, and will contribute toward addressing nutrition-related health issues.